Disease of Eye | Blindness
Signs
and Symptoms of Blindness
People who are
blind or have visible disability have the common sign of difficulty viewing. People who have similar stages of visual shortage may have very different responses with
that symptom. In case a
person is born blind, there is much
less adjustment to a non seeing entire
world compared to there is for those who lose their eyesight late in life, where there may be small capability to cope with that visual loss. Support systems available to human
beings and their psychological make-up will even change the symptom of lack of sight. Those
who lose their vision suddenly, rather
than during a period of years,
also can have more difficulty adjusting to their visual loss.
Associated signs
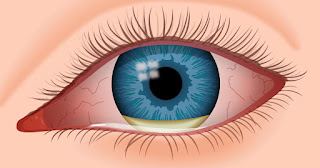
and symptoms, such a discomfort in the eyes,
awareness of the eyes, foreign body sensation, and ache in the eyes or discharge from the eyes may be
present or absent, based on the
underlying cause of the blindness.
Causes
of Blindness
The following eye diseases and conditions can create blindness:
- Glaucoma develops when the strain of the eye is enhanced and that brings about progressive loss of sight. It is essential to recognize and treat glaucoma as the vision lost is irreversible.
- Macular degeneration damages the portion of the eye that enables you to see details. It generally impacts older adults.
- Cataracts lead to cloudy vision. They’re more usual in seniors.
- Lazy eye makes it complicated to see details. It may bring about vision loss. Amblyopia is normally known as a “lazy eye”.
- Optic neuritis is inflammation which causes temporary or permanent vision loss.
- Retinitis pigmentosa means damage of the retina. It brings about blindness only in rare cases.
- Tumors that impact the retina or optic nerve can also result in blindness.
- Blindness is a possible complication when you have diabetes or have a stroke.
- Birth defects, eye injuries, and complications from eye surgery are some other typical reasons for blindness.
Who
is at Risk of Blindness
The following categories of persons are at risk of blindness:
- People who have eye diseases, for example macular degeneration and glaucoma
- People suffering from diabetes
- Anyone who has a stroke
- Eye surgery victims
- Individuals who work with or close to sharp objects or toxic chemicals
- Premature babies
Diagnosis
of Blindness
There are basically two major areas that are looked at when someone’s vision
is measured:
Visual Acuity: It
is central vision and is familiar to look
at objects in detail, for example reading
a book or watching video.
Visual Field: It
is the capability to see
around the edge of vision while looking straight ahead.
Visual
Field Testing:
During visual field testing one will
be directed to look straight ahead at a
machine while lights are flashed on and
off in peripheral vision . Person will be asked to press a button each
time you see a light. This shows any gaps
in his area of vision.
Test
for Visual Acuity:
A snellen chart is
utilized to determine visual acuity. It relates to reading letters off a chart on which the
letters turn into progressively smaller
sized. This chart is used during a routine eye
test. After the test, a score made up of two numbers is given. The first number shows the
distance far from the chart were able to successfully read the
letters on the chart. The second number shows the distance away a person with healthy vision should be able to read the
chart.
So if you were given a visual acuity
score of 6/60, this means you
can only look at 6 meters
away what a person with healthy eyesight can read 60 meters away. The
normal eyesight is 6/6.
Partial
sight impairment:
Partial sight, or sight impairment, is usually defined
as:
- Having very poor visible acuity ( 3/60 to 6/60 ) but having a full field of vision.
- Having a combination of moderate visual acuity ( up to 6/24 ) and a decreased field of vision or having blurriness or cloudiness in the central vision.
- Having relatively good visual acuity ( up to 6/18 ) but a lot of your field of vision is losing.
Severe
sight impairment (Blindness)
The legal meaning of
severe eyesight impairment (
blindness ) is when ‘a individual is
so blind that they cannot do
any work for which eye-sight is
essential’.
This normally falls
into one of three categories:
- Having extremely poor visual acuity ( lower than 3/60 ) but having the full field of vision
- Having inadequate visual acuity ( between 3/60 and 6/60 ) and a severe decrease in in the field of vision
- Having average visual acuity ( 6/60 or better ) and an extremely lowered field of vision
Treatment
of Blindness
A few of the
medical treatment possibilities and
the surgical treatment possibilities which are used to correct vision defects
and reduce loss include :
Conjunctivitis:
- Cleaning of the eyes
- Antibiotic droplets similar to chloramphenicol
- Using of dark goggles
Glaucoma
- Medical line of treatment-eye droplets & pills .
- Surgical
Corneal Ulcer
- Using eye drops. It is actually depend upon kind of ulcer
- Use of dark goggles
- Cleaning of eyes
- Rest to the sight by mydriatics
Iritis
Local Steroid eye drops and ointments,
cycloplegics, systemic steroids, ocular anti-hypertensive tablets.
Cataract
Surgery
Surgery
Refractive Errors
Providing Spectacles
Providing Spectacles
Trachoma
Tetracycline/Erythromycin eye ointment .
Tetracycline/Erythromycin eye ointment .
Retinopathy
Treatment of complication, control of diabetes & hypertension.
Treatment of complication, control of diabetes & hypertension.
Squint
Surgery, correction of refraction
Surgery, correction of refraction
Night Blindness
Treatment with vitamin A
Treatment with vitamin A
Corneal Opacity
Surgery
Surgery